 |
Acoustic Neuroma |
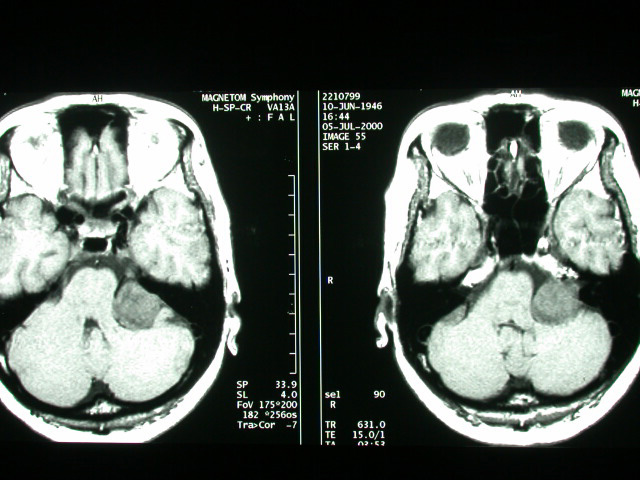
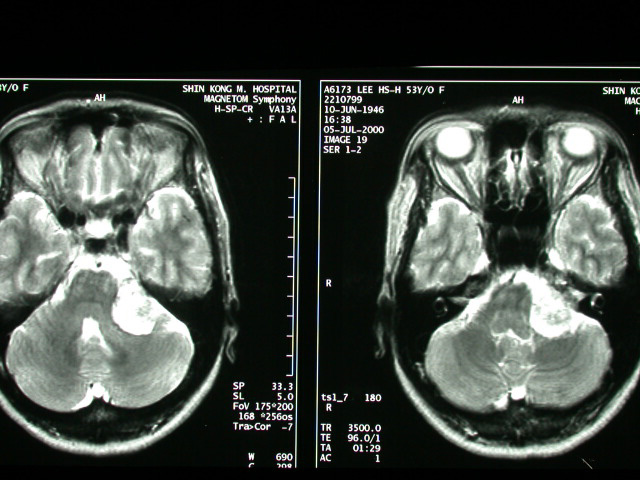
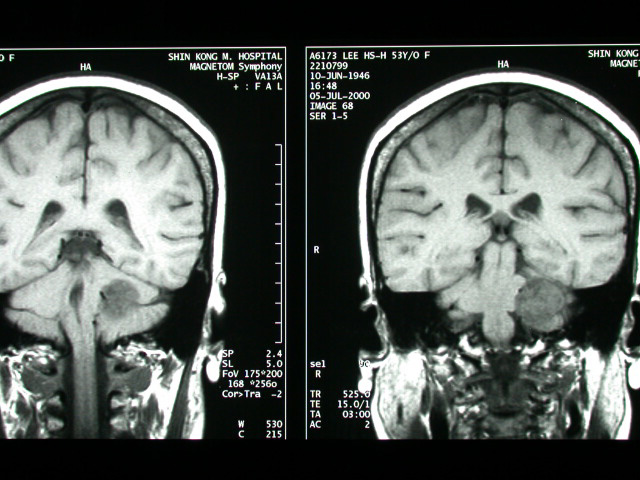
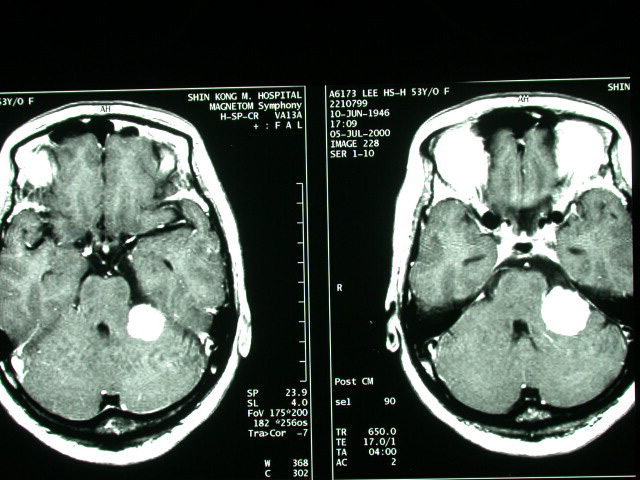
| History : This 54 year-old lady suffered from heaving impairment, ear tinnitus for half year. Image finding : An about 2.8cm well defined tumor at L't CPA with IAC extension & mass effect on the brain stem. Diagnosis : Acoustic neuroma with IAC extension, left. Discussion: Acoustic Neuroma =VESTIBULAR SCHWANNOMA = ACOUSTIC SCHWANNOMA = NEURILEMMOMA Most common neoplasm of internal auditory canal / cerebellopontine angle! Prevalence - :5-10% of all intracranial tumors; - 85% of all intracranial neuromas; -80-90% of all cerebellopontine angle tumors Age :(a)sporadic tumor: 35-60 years; M:F = 1:2 (b)type 2 neurofibromatosis: 2nd decade Histo: encapsulated neoplasm composed of proliferating fusiform Schwann cells with (a)highly cellular dense regions (Antoni A) with reticulin + collagen, and (b)loose areas with widely separated cells (Antoni B) in a reticulated myxoid matrix; - common degenerative changes with cyst formation, vascular features, lipid-laden foam cells -May be associated with:central neurofibromatosis - Solitary intracranial schwannoma is associated with type 2 neurofibromatosis in 5-25%! -Bilateral acoustic schwannomas allow a presumptive diagnosis of type 2 neurofibromatosis! -long history of slowly progressive unilateral sensorineural hearing loss affecting high-frequency sounds more severely (in 95%) tinnitus diminished corneal reflex unsteadiness, vertigo, ataxia, dizziness (<10%) pain Doubling time:2 years Location: (a)arises from within internal auditory canal (IAC) (b)may arise in cerebellopontine angle cistern at opening of IAC (= porus acusticus) with intracanalicular extension in 5% Site:(a)in 85% from the vestibular portion of 8th nerve (around vestibular ganglion of Scarpa / at the glial-Schwann cell junction) (b)in 15% from the cochlear portion -round mass centered on long axis of IAC forming acute angles with petrous bone funnel-shaped component extending into IAC - IAC enlargement / erosion (70-90%) widening / obliteration of ipsilateral cerebellopontine -angle cistern shift / asymmetry of 4th ventricle with hydrocephalus degenerative changes (cystic areas ± hemorrhage) with tumors >2-3 cm Plain film: erosion of IAC: a difference in canal height of >2 mm is abnormal + indicates a schwannoma in 93% CT: isodense small / hypodense large solid tumor cyst formation in tumor (= central necrosis) / adjacent to tumor (= extramural arachnoid cyst) in 15% of large tumors -usually uniformly dense tumor enhancement with small tumors (50% may be missed without CECT) / ring enhancement with large tumors - NO calcification intrathecal contrast / carbon dioxide insufflation (for tumors <5 mm) MR (most sensitive test with Gd-DTPA enhancement): iso- / slightly hypointense on T1WI relative to brain intensely enhancing homogeneous mass / ringlike enhancement (if cystic) after Gd-DTPA hyperintense on T2WI (DDx: meningioma remains hypo- / isointense) Angio: - elevation + posterior displacement of anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA) on basal view - elevation of the superior cerebellar artery (large tumors) displacement of basilar artery -anteriorly / posteriorly + contralateral side compression / posterior + lateral displacement of petrosal vein - posterior displacement of choroid point of PICA vascular supply frequently from external carotid artery branches rarely hypervascular tumor with tumor blush DDx:ossifying hemangioma (bony spiculations) |
|