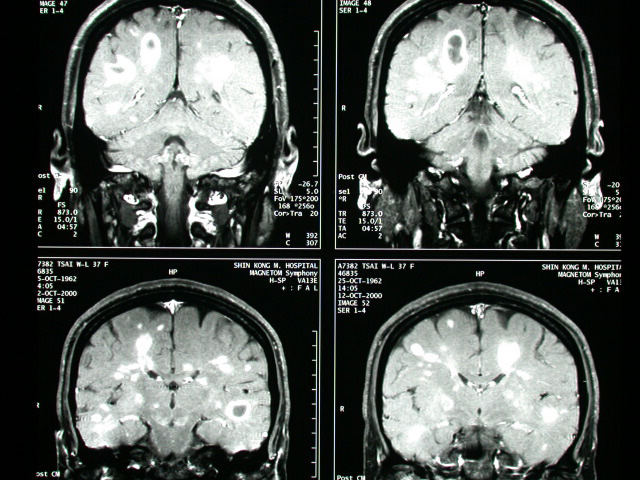
History :
This 37 y/o lady complained. Dizziness & unsteady gait for 1 month.
Image finding :
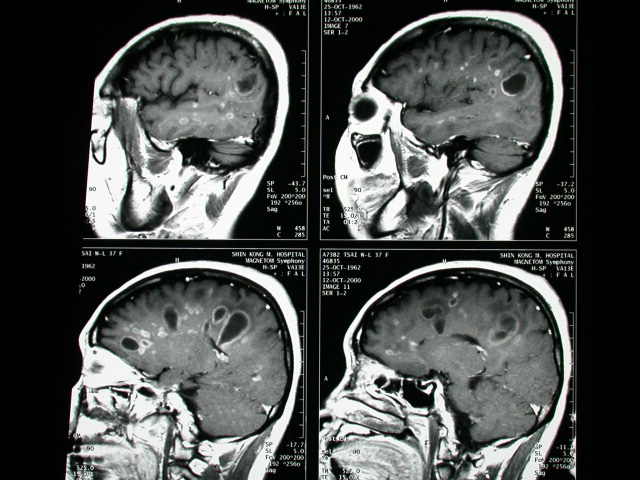
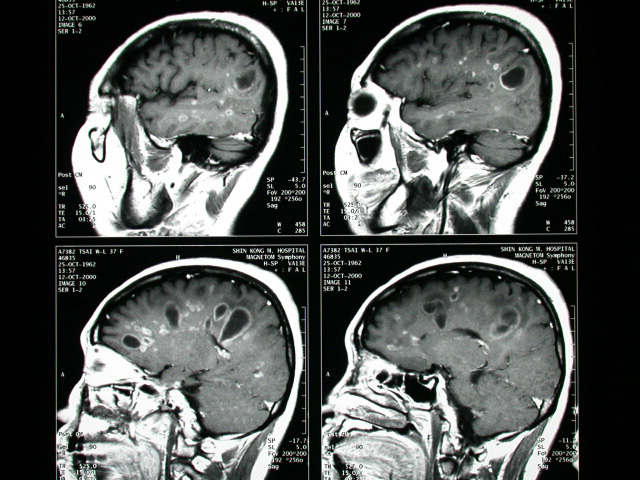
-MRI of brain showed multiple rim-like & nodularenhancing lesions
in WM of bil. Hemispheres.
-Several of them are oriented perpendicular to the ventricles lack
of
or minimal perifocal edema is shown
Diagnosis :
Multiple sclerosis
Discussion :
MULTIPE SCLEROSIS
=most frequent form of chronic inflammatory demyelinating disease
of unknown etiology, which reduces the lipid content and brain volume;
characterized by a relapsing + remitting course
Prevalence:
-6:10,000 (higher frequency in cooler climates; increased incidence
with positive family history)
Cause:? viral / autoimmune mechanism
Peak age:25-30 (range of 20-50) years; M:F = 2:3
Brain
-number + extent of plaques correlate with duration of disease +
degree of cognitive impairment
Location:
-subependymal periventricular location (along lateral aspects of
atria + occipital horns), corpus callosum, internal capsule, centrum
semiovale, corona radiata, optic nerves, chiasm, optic tract, brainstem
(ventrolateral aspect of pons at 5th nerve root entry), cerebellar
peduncles, cerebellum; rather symmetric involvement of cerebral
hemispheres; subcortical U fibers NOT spared
-lesion size: 1-25 (majority between 5 and 10) mm large lesions
may masquerade as brain tumors
-lesions usually without mass effect / edema unless acute
-ovoid lesions (86%) oriented with their long axis perpendicular
to ventricular walls (due to perivenous demyelination; pathologically
described as "Dawson fingers")
-chronic plaques do not enhance (due to intact blood-brain barrier)
CT:
-normal CT scan (18%)
-nonspecific atrophy of brain (45%): enlarged ventricles, prominent
sulci
-periventricular (near atria) multifocal nonconfluent lesions with
distinct margins (location not always correlating well with symptoms)
--(a)NECT:isodense / lucent
--(b)CECT:transient enhancement during acute stage (active demyelination)
for about 2 weeks; may require double dose of contrast; ultimately
disappearance / permanent scar
MR (modality of choice; 95% specific):
-well-marginated discrete foci of varying size with high-signal
intensity on T2WI + proton density images (= loss of hydrophobic
myelin produces increase in water content); hypointense on T1WI
-Gd-DTPA enhancement of lesions on T1WI (up to 8 weeks following
acute demyelination with breakdown of blood-brain barrier)
-lesions on undersurface of corpus callosum (CHARACTERISTIC sagittal
images) |