History :
A 77-year-old man suffered from sudden onset abdominal pain. The pain
was initially located in the epigastric region, but became diffuse
later. The patient had tarry stool history.
Questions:
1. What are the findings?
2. What is the diagnosis?
Answers:
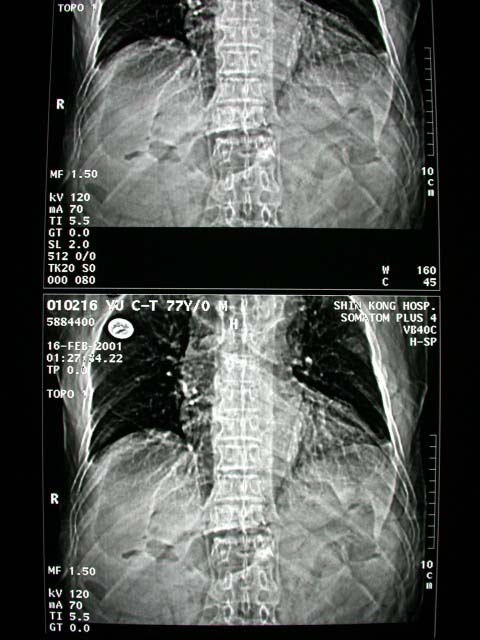
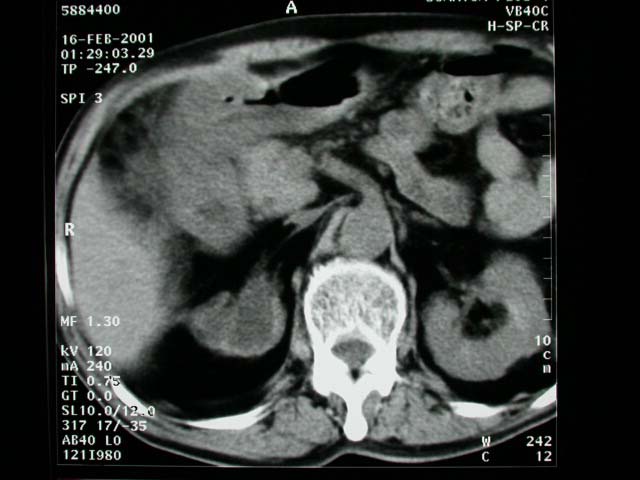
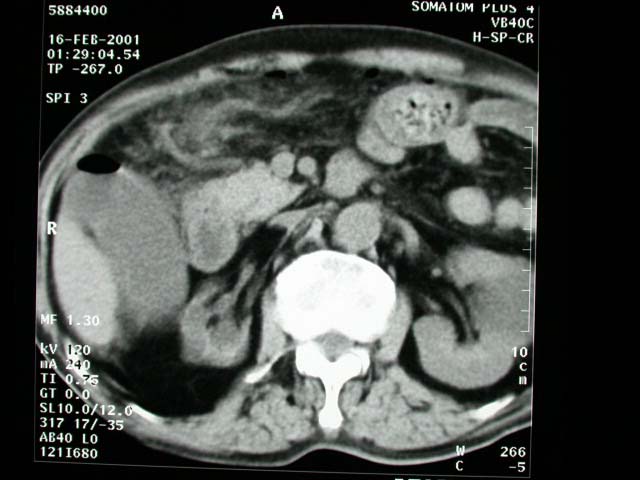
1. Plain abdominal film: Free air in the RUQ and epigastric region.
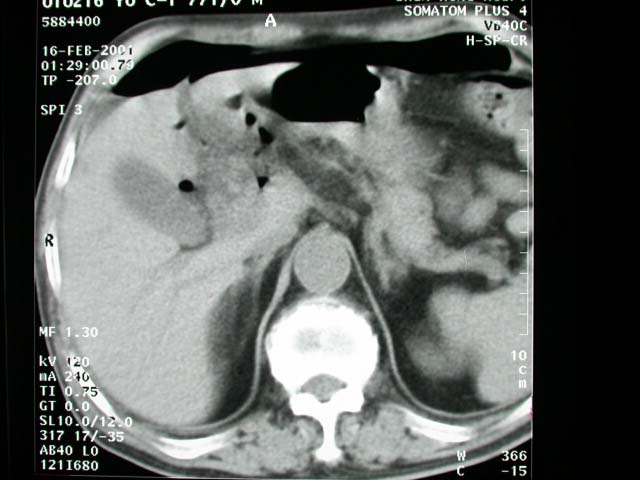
Precontrast abdominal CT: Free air in the abdominal cavity and surrounding
region of the duodenal cap, pyloric region and GB fossa. Dirty fat
plane is also noted in the surrounding area of duodenal cap and
RUQ. The right kidney is atrophic and hydronephrotic.
2. PPU (perforation of duodenal ulcer)
Discussion :
Large collection of gas:
-abdominal distension, no gastric air-fluid level
-"football sign" = large pneumoperitoneum outlining entire
abdominal cavity
-"double wall sign" = "Rigler sign" = "bas-relief
sign"
= air on both sides of bowel as intraluminal gas + free air outside
(usually requires >1,000 mL of free intraperitoneal gas + intraperitoneal
fluid)
-"telltale triangle sign" = triangular air pocket between
3 loops of bowel
-depiction of diaphragmatic muscle slips = two or three 6-13 cm
long and 8-10 mm wide arcuate soft-tissue bands directed vertically
inferiorly + arching parallel to diaphragmatic dome superiorly
-outline of ligaments of anterior inferior abdominal wall:
--"inverted V sign" = outline of both lateral umbilical
ligaments (containing inferior epigastric vessels)
--outline of medial umbilical ligaments (obliterated umbilical arteries)
--"urachus sign" = outline of middle umbilical ligament
RUQ gas (best place to look for small collections):
-single large area of hyperlucency over the liver
-oblique linear area of hyperlucency outlining the posteroinferior
margin of liver
-doge's cap sign = triangular collection of gas in Morison pouch
(posterior hepatorenal space)
-outline of falciform ligament = long vertical line to the right
of midline extending from ligamentum teres notch to umbilicus; most
common structure outlined
-ligamentum teres notch = inverted V-shaped area of hyperlucency
along undersurface of liver
-ligamentum teres sign = air outlining fissure of ligamentum teres
hepatis (= posterior free edge of falciform ligament) seen as vertically
oriented sharply defined slitlike / oval area of hyperlucency between
10th and 12th rib within 2.5-4.0 cm of right vertebral border 2-7
mm wide and 6-20 mm long
-"saddlebag / mustache / cupola sign" = gas trapped below
central tendon of diaphragm
-parahepatic air = gas bubble lateral to right edge of liver
|