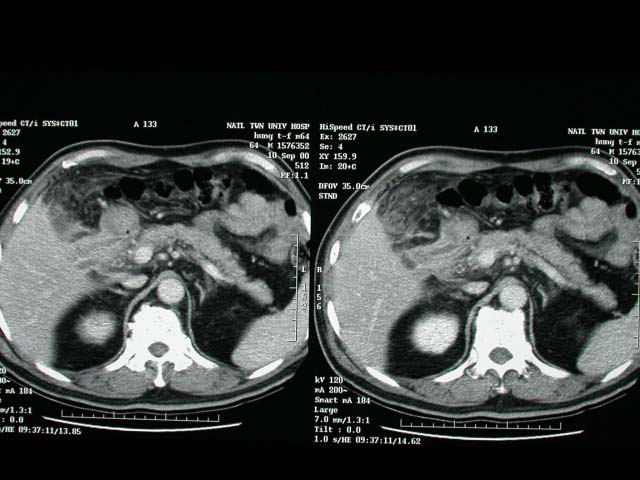
History :
The 64 y/o male suffered from abdominal pain without nausea,vomiting
and diarrhea.
Image finding :
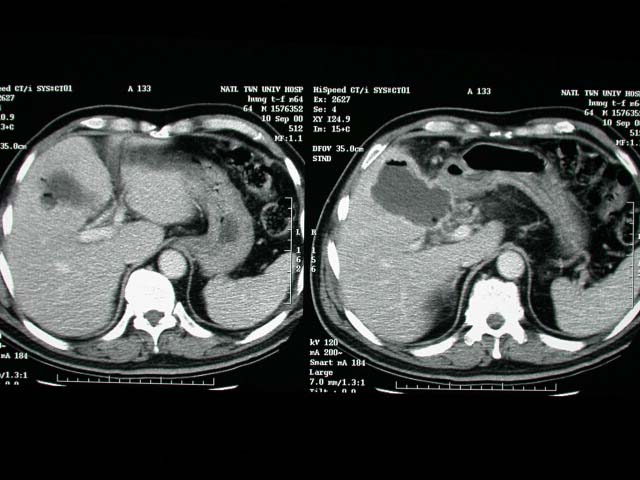
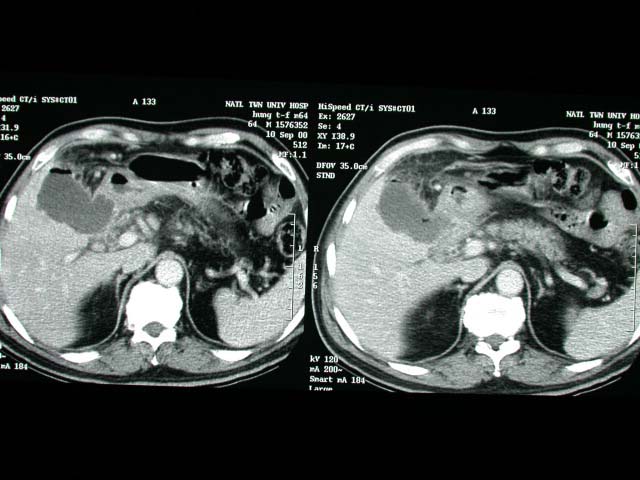
GB wall thickening with rupture into GB bed. Severe adhesion around
GB. White bile(+) with pus in GB.
Diagnosis :
Acute cholecystitis.
Discussion :
Acute Cholecystitis
Etiology:
-(a)in 80-95% cystic duct obstruction by impacted calculus; 85%
disimpact spontaneously
-(b)in 10% acalculous cholecystitis
Pathogenesis:
-chemical irritation from concentrated bile, bacterial infection,
reflux of pancreatic secretions
Age peak:
-5th-6th decade; M:F = 1:3
persisting (>6 hours) RUQ pain radiating to right shoulder /
scapula / interscapular area (DDx: biliary colic usually <6 hours)
nausea, vomiting, chills, fever RUQ tenderness + guarding
leukocytosis, elevated levels of alkaline phosphatase and transaminase
and amylase
mild hyperbilirubinemia (20%)
Murphy sign = inspiratory arrest upon palpation of GB area (falsely
positive in 6% of patients with cholelithiasis)
Cx:
(1)Gangrene of gallbladder
-shaggy, irregular, asymmetric wall (mucosal ulcers, intraluminal
hemorrhage, necrosis)
-hyperechoic foci within GB wall (microabscesses in Rokitansky-Aschoff
sinuses)
-intraluminal pseudomembranes (gangrene)
-coarse nonshadowing nondependent echodensities (= sloughed necrotic
mucosa / sludge / pus / clotted blood within gallbladder)
(2)Perforation of gallbladder (in 2-20%)
-(a)acute free perforation with peritonitis causing pericholecystic
abscess in 33%
-(b)subacute localized perforation causing pericholecystic abscess
in 48% (
-c)chronic perforation resulting in internal biliary fistula causing
pericholecystic abscess in 18%
Location: most commonly perforation of fundus gallstone lying free
in peritoneal cavity sonolucent / complex collection surrounding
GB
(3)Empyema of gallbladder multiple medium / coarse highly reflective
intraluminal echoes without shadowing / layering / gravity dependence
(purulent exudate / debris) |