|
History :
This 73 y/o gentleman had vague abdominal fullness sensation for
one
year.
Diagnosis :
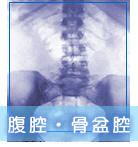
Polycystic diseases, bilateral kidneys and liver cyst
Discussion :
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
=ADULT POLYCYSTIC KIDNEY DISEASE
=Potter Type III
=slowly progressive disease with nearly 100% penetrance and great
variation in expressivity
Cause:
-gene located on short arm of chromosome 16 (in 90%)
-spontaneous mutation in 10%
Incidence:
1:1,000 people carry the mutant gene; 3rd most prevalent cause of
chronic renal failure
Associated with:
(1)Cysts in: liver (25-50%), pancreas (9%); rare in lung, spleen,
thyroid, ovaries, uterus, testis, seminal vesicles, epididymis,
bladder
(2)Aneurysm: saccular "berry" aneurysm of cerebral arteries
(3-13%)
(3)Mitral valve prolapse
-symptomatic at mean age of 35 years (cysts are growing with age)
-hypertension (50-70%)
-azotemia
-hematuria, proteinuria
-lumbar / abdominal pain
-bilaterally large kidneys with multifocal round lesions; unilateral
enlargement may be the first manifestation of the disease
-cysts may calcify in curvilinear rim- / ringlike irregular amorphous
fashion
-elongated + distorted + attenuated collecting system
-nodular puddling of contrast material on delayed images
-"Swiss cheese" nephrogram = multiple lesions of varying
size with smooth margins
-polycystic kidneys shrink after beginning of renal failure, after
renal transplantation, or on chronic hemodialysis
NUC:
-poor renal function on Tc-99m DTPA scan
-multiple areas of diminished activity, cortical activity only in
areas of functioning cortex |